Nutrition for Children: A Guide to Healthy Eating Habits
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on nutrition for children! As parents and caregivers, ensuring that our kids eat healthily can be a challenging yet essential part of upbringing. This post aims to shed light on the importance of balanced nutrition for children and offer practical tips to incorporate it into their daily lives.
Why is Nutrition Important for Children?
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in the growth and development of children. A balanced diet helps in:
- Physical Development: Adequate nutrition is crucial for the physical growth of children, including bone and muscle development.
- Cognitive Functioning: Proper nutrition is linked to improved concentration, memory, and cognitive development.
- Immune System Support: A healthy diet strengthens the immune system, helping children ward off illnesses.
- Energy Levels: Balanced meals provide children with the energy needed for their daily activities and play.
Understanding the Basics of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet for children includes a mix of:
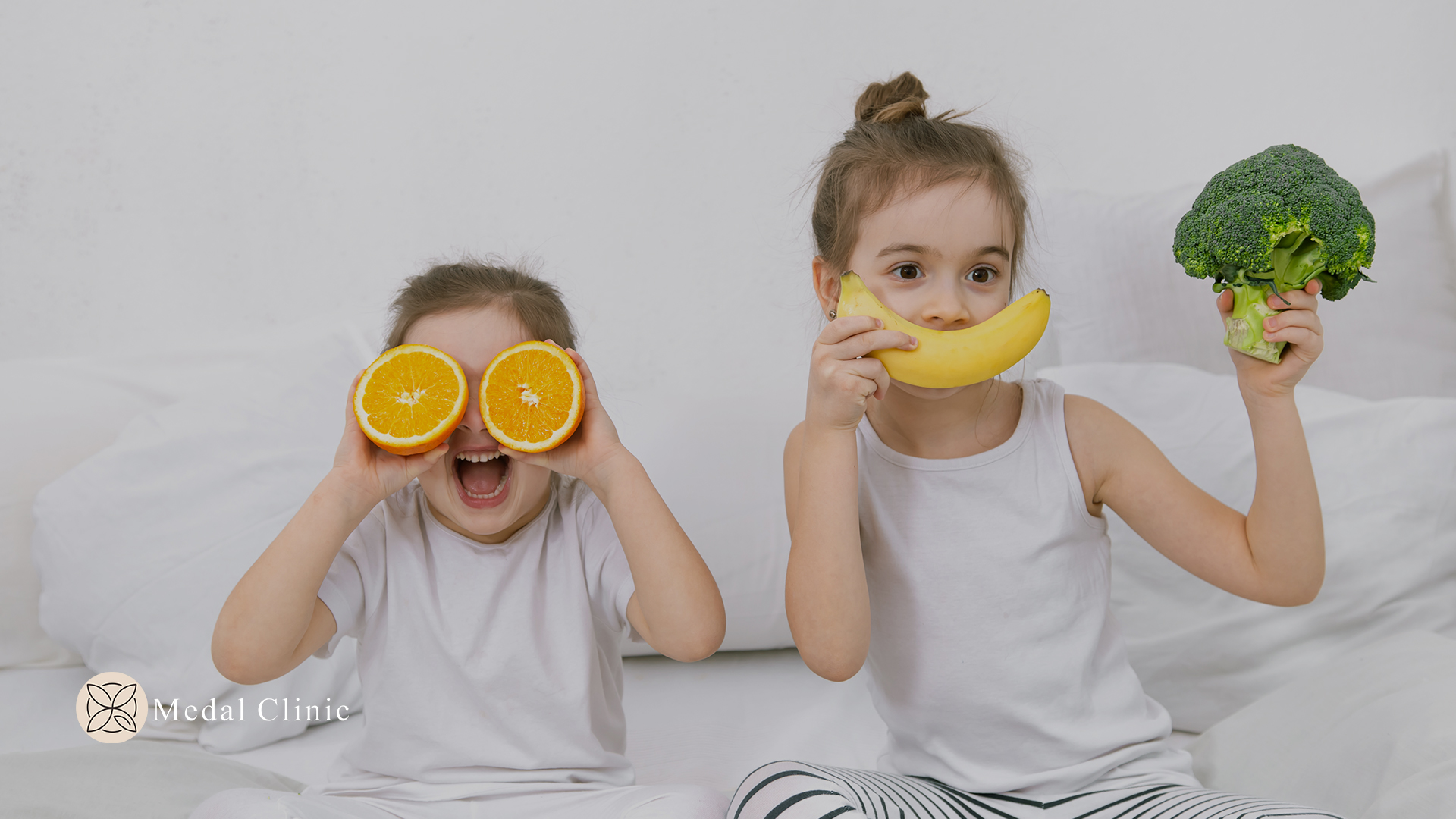
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Proteins: Essential for growth and repair. Sources include meat, fish, eggs, and plant-based options like beans and lentils.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy. Opt for whole grains like brown rice, whole wheat bread, and oats.
- Dairy or Alternatives: Important for calcium and vitamin D, crucial for bone health.
- Healthy Fats: Found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and oily fish, they are vital for brain development.
Age-Specific Nutritional Needs
- Toddlers (1-3 years): Focus on iron-rich foods and whole fruits.
- Preschoolers (4-6 years): Introduce a variety of food groups and textures.
- School-Aged Children (7-12 years): Emphasize balanced meals to support growth spurts.
- Teenagers: Cater to increased nutritional needs due to puberty and growth.
Tips for Encouraging Healthy Eating Habits
- Lead by Example: Children mimic adults. Eating healthy meals together sets a positive example.
- Involve Children in Meal Planning: Let them choose fruits or vegetables to include in meals.
- Make Healthy Foods Fun: Present meals in creative ways to make them appealing.
- Limit Sugary and Processed Foods: Encourage natural snacks over sugary options.
- Educate About Food Choices: Teach children about the benefits of various foods.
Overcoming Challenges
- Picky Eaters: Introduce new foods gradually and in small portions.
- Busy Schedules: Plan meals ahead and consider healthy, quick options.
- Budget Constraints: Focus on seasonal produce and bulk buying for savings.
Conclusion
Nutrition for children is a cornerstone for a healthy, active life. By instilling good eating habits from a young age, we can set the foundation for their well-being. Remember, every small step towards a balanced diet counts in nurturing healthier, happier children.
FAQ's
What are the key components of a balanced diet for children?
A balanced diet for children should include a variety of foods from all the major food groups: fruits and vegetables for vitamins and minerals, whole grains for energy, proteins (from both animal and plant sources) for growth and repair, dairy or dairy alternatives for calcium and vitamin D, and small amounts of healthy fats for brain development. The proportions of these groups can vary depending on the child’s age, activity level, and health needs.
How can I encourage my child to eat more fruits and vegetables?
Encouraging children to eat more fruits and vegetables can be achieved by involving them in the selection process, presenting the food in fun and visually appealing ways, and setting a good example by eating fruits and vegetables yourself. Additionally, offering a variety of choices, incorporating fruits and vegetables into favorite dishes, and providing them as snacks are effective strategies.
What should I do if my child is a picky eater?
Dealing with picky eaters involves patience and creativity. Introduce new foods gradually, pair them with familiar favorites, and avoid forcing the child to eat. Offering a variety of foods and creating a positive mealtime atmosphere can also help. Remember, it’s normal for children’s appetites to vary and it may take multiple exposures to a new food before they accept it.
Are supplements necessary for children?
In most cases, children can get all the nutrients they need from a balanced diet. However, some children may need supplements, especially if they have dietary restrictions (like veganism), health conditions, or are extremely picky eaters. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or a pediatric nutritionist before starting any supplements.
How can I ensure my child is getting enough protein if they're vegetarian or vegan?
Vegetarian and vegan diets can provide enough protein for children if planned carefully. Include a variety of plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, tofu, tempeh, edamame, and certain whole grains like quinoa. Fortified plant milks and protein-rich vegetables can also contribute to meeting protein needs. Again, consulting with a nutritionist can ensure the diet is balanced and adequate in all nutrients.