Understanding Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of a Balanced Diet
In the quest for a healthy lifestyle, one cannot underestimate the significance of a well-balanced diet. A key aspect of this is understanding macronutrients, the essential components that provide energy and support various bodily functions. Macronutrients, namely carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, play crucial roles in our overall health and well-being. By comprehending their functions, sources, and recommended intake, individuals can make informed dietary choices to achieve optimal nutrition. In this blog, we delve into the world of macronutrients and unravel their importance in maintaining a balanced diet.
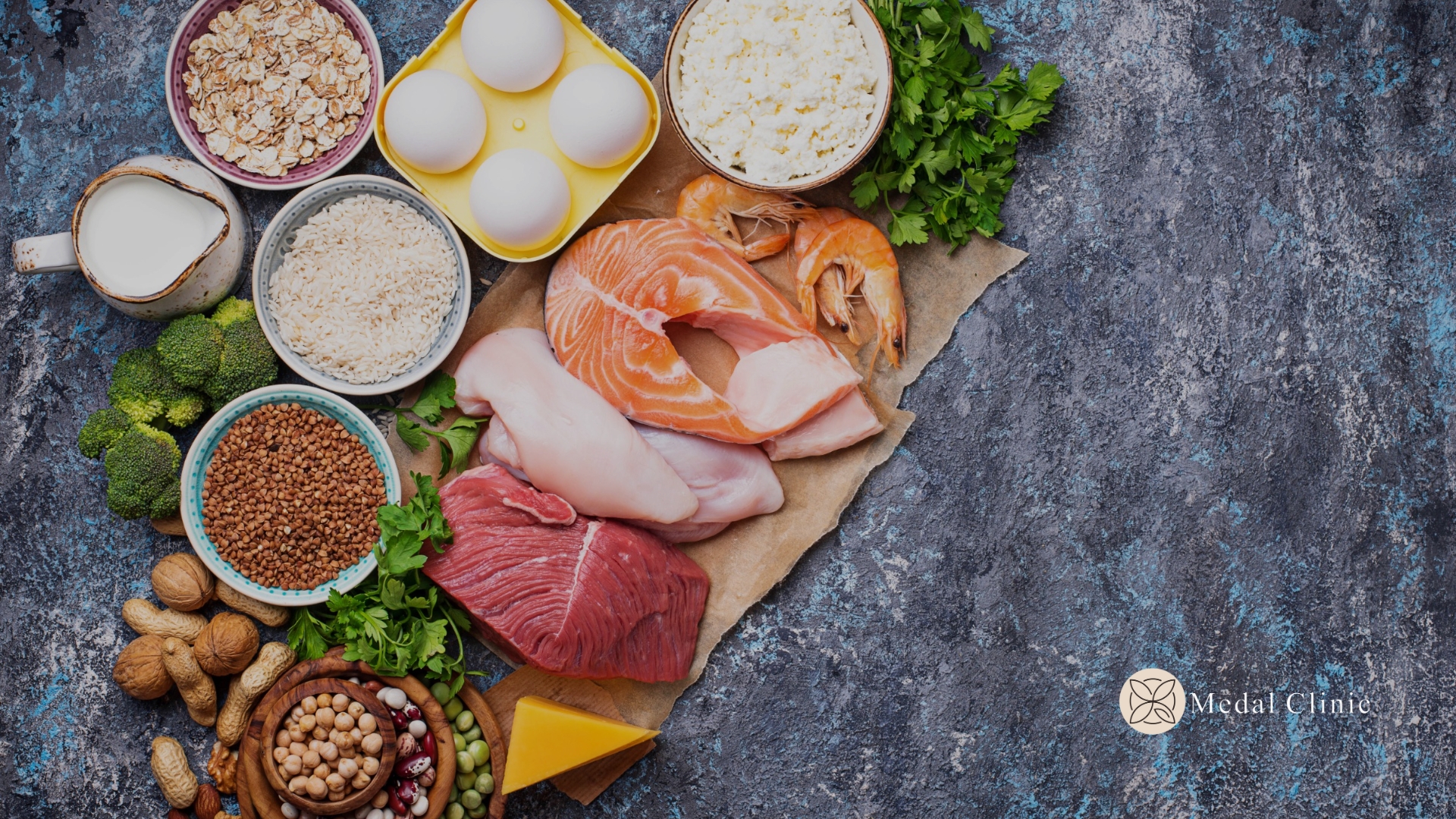
Carbohydrates: The Body’s Primary Fuel Source Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy, providing fuel for the brain, muscles, and other bodily functions. They are classified into two types: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates, found in fruits, sugar, and processed foods, are quickly absorbed and provide rapid bursts of energy. However, their consumption should be moderated due to their high sugar content.
On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, present in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, are digested more slowly, providing sustained energy and promoting feelings of fullness. These nutrient-dense foods also offer fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making them an essential part of a balanced diet. It is advisable to focus on complex carbohydrates, incorporating whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats, as well as a variety of fruits and vegetables into daily meals.
Proteins: The Building Blocks of Life Proteins are crucial for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues, including muscles, organs, and the immune system. They are composed of amino acids, which are vital for numerous physiological processes. Protein-rich foods include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Consuming a variety of protein sources ensures an adequate intake of all essential amino acids. While animal-based proteins provide a complete set of amino acids, plant-based proteins can be combined strategically to achieve the same effect. It is recommended to incorporate lean proteins into meals while considering individual dietary preferences, including vegetarian and vegan options.
Fats: Essential for Health and Vital Functions Contrary to common misconceptions, fats are essential for the body’s overall health. They provide energy, aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, protect organs, and support brain function. Fats are classified into saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats.
Saturated fats, found in animal products and some tropical oils, should be consumed in moderation, as excessive intake can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are considered healthier options and can be found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
Trans fats, often found in processed and fried foods, should be avoided altogether, as they are linked to various health issues. Striking a balance between different types of fats is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet.
Achieving a Balanced Macronutrient Ratio: While macronutrient requirements vary depending on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and individual goals, a balanced diet typically consists of a moderate intake of carbohydrates, an adequate amount of proteins, and a healthy proportion of fats. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommend a macronutrient distribution of around 45-65% of calories from carbohydrates, 10-35% from protein, and 20-35% from fats.
However, it is important to note that these ranges are general recommendations and may vary based on individual needs. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance based on specific requirements.
Understanding macronutrients and their roles in our diet is essential for maintaining optimal health. A balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats provides the body with the energy and nutrients necessary for its proper functioning. By incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods into our daily meals, we can ensure we are meeting our macronutrient needs while enjoying a diverse and satisfying diet. Remember, balance is key when it comes to achieving a healthy lifestyle.
FAQ's
What are macronutrients?
Macronutrients are the three essential components of our diet that provide energy and support various bodily functions. They include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
What is the role of carbohydrates in our diet?
Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They fuel our brain, muscles, and other bodily functions. Carbohydrates can be categorized into simple and complex forms, with complex carbohydrates being more beneficial due to their slower digestion and additional nutrients.
Why are proteins important in our diet?
Proteins are the building blocks of life and are vital for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues. They support muscle development, aid in the immune system’s functioning, and participate in various physiological processes.
What are good sources of protein?
Good sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Animal-based proteins typically provide all essential amino acids, while plant-based proteins can be combined strategically to achieve the same effect.
Are fats bad for our health?
No, fats are not inherently bad for our health. In fact, they are essential for the body’s overall well-being. Fats provide energy, aid in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, protect organs, and support brain function. However, it is important to choose healthier fats, such as unsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, and limit the intake of saturated and trans fats.
How can I achieve a balanced macronutrient ratio?
A balanced macronutrient ratio varies based on individual factors, but a general guideline is to consume around 45-65% of calories from carbohydrates, 10-35% from protein, and 20-35% from fats. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance based on your specific needs and goals
Can I follow a specific macronutrient ratio for weight loss?
While some individuals may choose to follow specific macronutrient ratios for weight loss, it is important to approach weight loss in a balanced and sustainable manner. It is advisable to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or registered dietitian who can create a personalized plan based on your individual needs and goals.
Can I consume too much of a specific macronutrient?
Yes, excessive consumption of any macronutrient can have negative effects on health. For example, consuming too many carbohydrates or fats without considering portion sizes and overall calorie intake can lead to weight gain and other health issues. It’s important to focus on moderation and balance when it comes to macronutrient intake.
Are there any specific macronutrient requirements for athletes?
Athletes may have higher energy and nutrient needs due to their increased activity levels. It is advisable for athletes to work with a sports nutritionist or registered dietitian who can provide tailored advice to meet their specific macronutrient requirements and optimize their performance.
Can I meet my macronutrient needs on a vegetarian or vegan diet?
Yes, it is possible to meet macronutrient needs on a vegetarian or vegan diet by incorporating a variety of plant-based protein sources. Plant-based proteins can be combined strategically to ensure a complete set of essential amino acids. Consulting a registered dietitian can help in planning a well-balanced vegetarian or vegan diet that meets all nutritional needs.