Summer Diarrhea in Children: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
The scorching heat of summer not only brings the joys of outdoor activities and vacations but also poses certain health risks, especially for children. One common health concern during the summer season is diarrhea, which can significantly impact the well-being of young ones. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies for summer diarrhea in children. By understanding this condition and implementing preventive measures, parents and caregivers can ensure their children stay healthy and enjoy a delightful summer.
What Is Summer Diarrhea in Children?
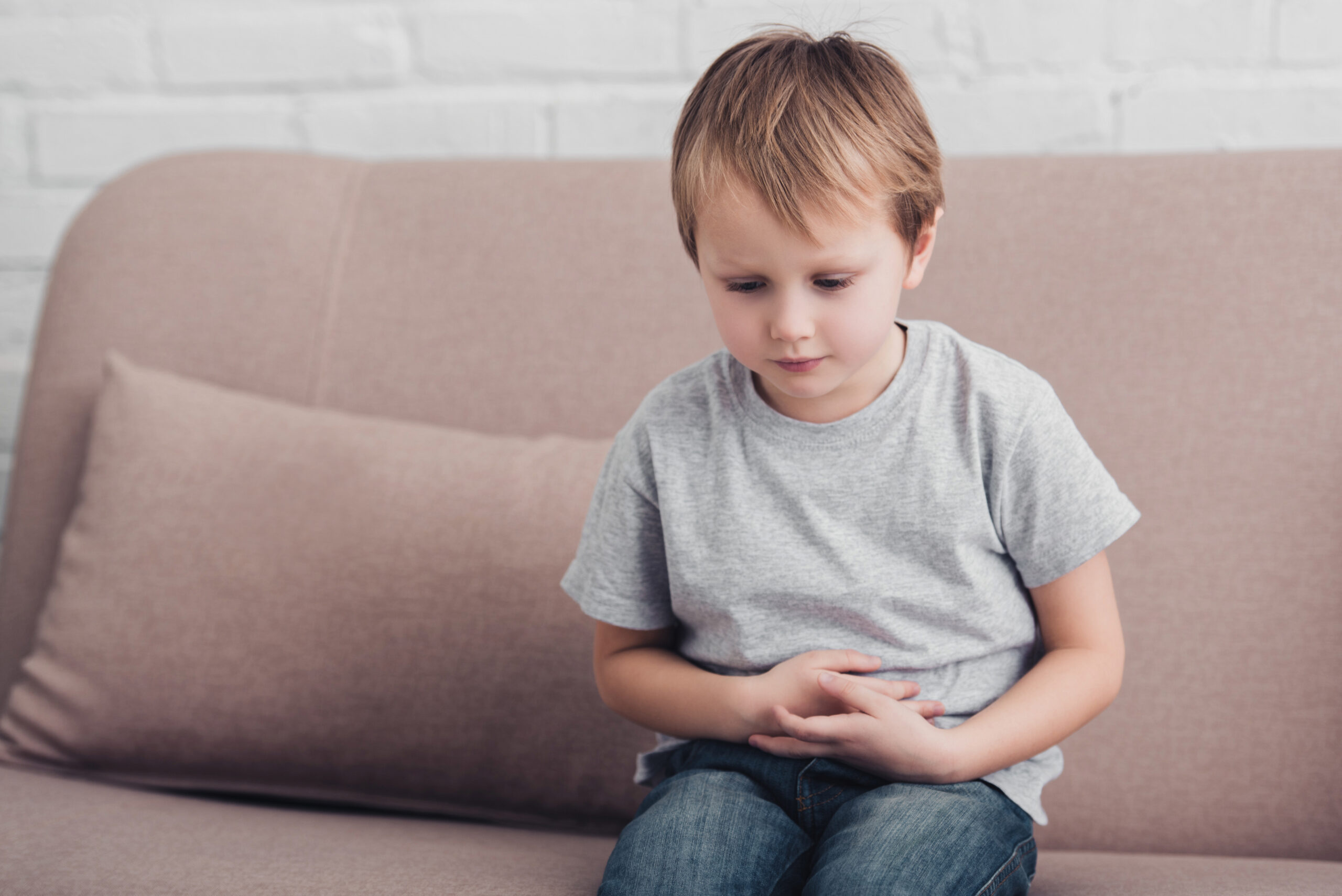
Summer diarrhea, commonly known as summer diarrhea, refers to the increased frequency and fluidity of bowel movements in children during the summer months. It is typically caused by the ingestion of contaminated food or water, leading to an infection in the gastrointestinal tract. The condition is more prevalent in warmer climates and often occurs due to improper food handling, inadequate sanitation, and poor personal hygiene practices.
Causes of Summer Diarrhea in Children
1- Bacterial Infections:
- Consuming contaminated food or water, such as improperly cooked meat, unpasteurized milk, or unhygienic street food, can introduce harmful bacteria into the child’s digestive system. Common bacterial culprits include Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella, and Campylobacter.
2- Viral Infections:
- Viruses like rotavirus, norovirus, and adenovirus can cause gastroenteritis, leading to diarrhea. These viruses are highly contagious and can spread through person-to-person contact or by ingesting contaminated food or water.
3- Parasitic Infections:
- Parasitic organisms like Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium can contaminate water sources, especially swimming pools, lakes, and recreational water areas. When children come into contact with these parasites, they may develop diarrhea.
4- Food Poisoning:
- Consumption of spoiled or contaminated food can lead to food poisoning, triggering diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms. Improper food storage, inadequate refrigeration, and cross-contamination are common causes of food poisoning during the summer.
5- Heat-related Factors:
- Excessive heat and humidity can contribute to dehydration, which can worsen diarrhea symptoms. Sweating profusely and not drinking enough fluids can lead to electrolyte imbalances and increased vulnerability to diarrhea.
Symptoms of Summer Diarrhea in Children
Summer diarrhea in children is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Frequent loose or watery stools
- Abdominal cramps and pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever (sometimes)
- Dehydration (dry mouth, decreased urine output, sunken eyes, lethargy)
Prevention Strategies
To minimize the risk of summer diarrhea in children, it is crucial to adopt preventive measures. Consider the following strategies:
1- Safe Food and Water:
- Ensure that your child consumes safe, properly cooked food. Avoid street food and unpasteurized dairy products. Encourage handwashing before meals and teach children about food hygiene. Offer bottled or boiled water when tap water quality is questionable.
2- Good Hygiene Practices:
- Teach children the importance of hand hygiene, especially before eating and after using the toilet. Use soap and clean water for at least 20 seconds.
3- Proper Food Storage and Preparation:
- Store food properly to prevent bacterial growth. Refrigerate perishable items promptly and discard any spoiled food. Thoroughly wash fruits and vegetables before consumption. Cook meat and seafood thoroughly to kill any harmful bacteria.
4- Maintain Hydration:
- Encourage your child to drink an adequate amount of fluids, especially water, throughout the day. Offer hydrating options like fresh fruit juices, coconut water, and oral rehydration solutions (ORS) to replenish lost electrolytes during diarrhea.
5- Avoid Contaminated Recreational Water:
- Teach children to avoid swallowing water while swimming in pools, lakes, or other recreational water areas. Ensure that swimming pools are properly maintained and chlorinated to reduce the risk of parasitic infections.
6- Sun Protection:
- Protect your child from excessive heat and sun exposure, as this can contribute to dehydration and worsen diarrhea symptoms. Use sunscreen, dress them in light and breathable clothing, and encourage them to seek shade during peak sun hours.
7- Regular Handwashing:
- Emphasize the importance of frequent handwashing with soap and water, especially after using the toilet, playing outdoors, or coming into contact with potentially contaminated surfaces.
8- Stay Updated on Vaccinations:
- Ensure that your child is up to date with vaccinations, including the rotavirus vaccine. This vaccine can significantly reduce the risk of diarrhea caused by rotavirus infection.
In Conclusion
Summer diarrhea in children can be a distressing condition, but with proper knowledge and preventive measures, it can be mitigated. By promoting good hygiene practices, ensuring food and water safety, and maintaining adequate hydration, parents and caregivers can protect their children from summer diarrhea. Remember to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. Let’s make this summer a healthy and enjoyable season for our little ones. Stay informed, stay safe!
FAQ's
How long does summer diarrhea usually last in children?
The duration of summer diarrhea can vary, but most cases resolve within a few days to a week. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional.
When should I seek medical attention for my child with summer diarrhea?
It is recommended to seek medical attention if your child shows signs of dehydration, such as decreased urine output, lethargy, or sunken eyes. Additionally, if the diarrhea is persistent, accompanied by severe abdominal pain or blood in the stool, medical evaluation is necessary.
Can probiotics help prevent or treat summer diarrhea in children?
Probiotics, particularly certain strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, have shown potential in preventing and managing diarrhea. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before giving probiotics to children.